Unit 2 Lab 2 Making Art by Using Data Structures Page 2
Planning a Quiz App
On this page, y'all volition brainstorm to develop a quiz app by creating an abstruse data type to pair the questions with their answers.
: Sublist
A sublist is a list used as an item of some other list.
(The word sublist is as well used to refer to some subset of a list.)


Just code like  is hard to read and understand. A better way is to use abstraction to organize the quiz items. The brainchild merely hides the
is hard to read and understand. A better way is to use abstraction to organize the quiz items. The brainchild merely hides the list and item of blocks, and so it isn't complicated to build, but it can brand your code much easier to write, read, and debug.


: Data Types
- A information type is what kind of information something is (number, text string, list, etc.). For case, number is the data type for the starting time input to
 and list is the the data type for its second input.
and list is the the data type for its second input. - Each programming language provides some primitive data types (data types that are built-in). For example, Snap! provides numbers, text (words and sentences), Booleans (true or false), lists, and some you oasis't all the same used as data (such every bit sprites and costumes). This bill of fare shows all of Snap!'due south primitive types.

: Abstract Data Types
The constructor and selector together implement the quiz item abstract data type.
- Data abstraction is the creation and employ of abstract data types in a plan.
-
"U2L2-Quiz"

- Build the custom
quiz itemabstract data type (both the constructor and the two selectors). - Click on the pointer to the right of the input name:
- Choose the information blazon you want for that input. (For this project, you'll use the "text" and "list" input types.)
- Click "OK."
- Create a global variable to store your quiz items and initialize it equally a listing of items, using your constructor where appropriate.
- Test both the selectors for different items in your listing of quiz items, and debug any problems.
-
Imagine you make a variable capitals and apply
setto requite this list of lists a name:
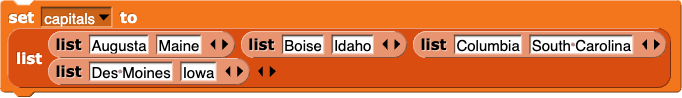
Which of the following statements are truthful?Cull all that apply.
 reports a listing with two items: "Augusta" and "Maine".
reports a listing with two items: "Augusta" and "Maine". Correct.
 reports the word "Augusta".
reports the word "Augusta". Correct.
 reports the discussion "Iowa".
reports the discussion "Iowa". No. What is item two of "capitals"?
 reports the number 8.
reports the number 8. No. Each of the pocket-sized lists is a unmarried item in the list "capitals" .
 reports a list with one item: "Iowa".
reports a list with one item: "Iowa". Correct.
 reports the string "Boise".
reports the string "Boise". The items of capitals are lists.
 reports the string "Iowa".
reports the string "Iowa". The items of
all but kickoff of (capitals)are lists. reports the number two.
reports the number two. Right.
Specifying an Input Blazon
Your selectors expect a quiz item, i.e., a list, as input. You tin make your blocks testify what type of information they wait. It's not necessary in Snap! but, like assigning a color to a cake, it can exist a helpful reminder of what the block does and what type of input it expects. You've already seen input slots of several shapes, indicating different expected information types.
In the Block Editor while creating a selector, click on a plus sign to enter an input proper name. Then...
Snap! has two different views for lists within lists. You lot can switch which view yous come across past correct-clicking (or command-clicking) on the quiz watcher (or whatever you chosen the variable) on the stage.
If you don't see the watcher on the stage, make sure the checkbox beside the quiz variable in the Variables palette is checked. 
: Table
A table is a two-dimensional information structure with rows and columns. If you lot've used a spreadsheet program, what it displays is a table.
In Snap!, a table is implemented as a list of lists, in which each sublist is one row of the table.
Source: https://bjc.edc.org/bjc-r/cur/programming/2-complexity/2-data-structures-art/2-quizzes.html?topic=nyc_bjc%2F2-conditionals-abstraction.topic&course=bjc4nyc.html&novideo&noassignment
0 Response to "Unit 2 Lab 2 Making Art by Using Data Structures Page 2"
Post a Comment